Pi-Hole Guide
1. Installation
Docker installation reference documentation can be found here
-
Create a folder
mkdir -p ./repo-docker-master/stack-networking -
Change current directory
cd ./repo-docker-master/stack-networking -
Create a Docker compose file
Expand for
docker-compose.ymlcontentsversion: "3" services: # More info at https://github.com/pi-hole/docker-pi-hole/ and https://docs.pi-hole.net/ pihole: container_name: Pi-hole image: pihole/pihole:latest ports: - "8082:80/tcp" # UI - "53:53/tcp" - "53:53/udp" #- "67:67/udp" # Only required if you are using Pi-hole as your DHCP server environment: - TZ=America/New_York - DNSMASQ_LISTENING=all # Volumes store your data between container upgrades volumes: - ./Pi-hole-data/etc-pihole:/etc/pihole - ./Pi-hole-data/etc-dnsmasq.d:/etc/dnsmasq.d # https://github.com/pi-hole/docker-pi-hole#note-on-capabilities #cap_add: # - NET_ADMIN # Required if you are using Pi-hole as your DHCP server, else not needed restart: always -
Start the Docker container
sudo docker-compose up -dThis will fail to start since port 53 is already bound to the systemd-resolved.service.
We’ll disable this in the next step…
2. Disable DNS Server
-
By default port 53 is tied to the
caching DNS stub resolverservice.sudo ss -ltnp | grep :53 LISTEN 0 32 xxx.xxx.xxx.x:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("dnsmasq",pid=8108,fd=6)) LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.53%lo:53 0.0.0.0:* users:(("systemd-resolve",pid=3691922,fd=14)) -
Disable the service
sudo systemctl disable systemd-resolved.service -
Stop the service
sudo systemctl stop systemd-resolved.service -
Edit
resolv.conf-
Open the file
sudo vi /etc/resolv.conf -
Update the name server
Like so#nameserver 127.0.0.53 nameserver x.x.x.x (1) nameserver 8.8.8.8 (2)1 This is the router’s IP address.
We’ll hard-code this for now untilPi-holeis configured as the DHCP server.2 Google Public DNS.
-
-
Now restart the container
sudo docker-compose up -d
3. Configuration
3.1. Configure Pi-hole
3.1.1. Password
Get the randomly generated admin password or set it to a new value.
-
Get the password
sudo docker logs Pi-hole | grep passwordExample 1. Outputsudo docker logs Pi-hole | grep password
s6-rc: info: service _startup: starting
[i] Assigning random password: YOhz14Lq
[✓] New password set -
Set the password
sudo docker exec -it Pi-hole pihole -a -pExample 2. Outputsudo docker exec -it Pi-hole pihole -a -p
Enter New Password (Blank for no password):
Confirm Password:
[✓] New password set
3.2. Configure Router
3.2.1. DNS Settings
-
The DNS configuration in the router needs to point to the IP address of the server hosting the docker Pi-hole container.
Typically, this is already set to your internet service provider’s DNS servers, but it should be updated with the IP address of the server that hosts Pi-hole container.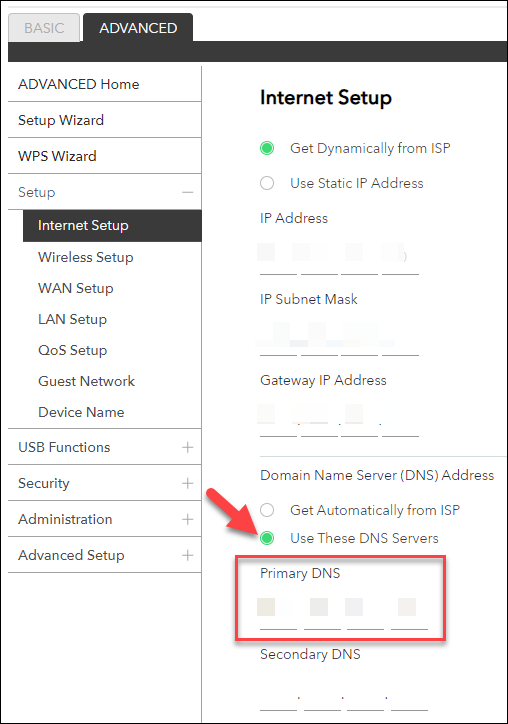
-
Configure the router to use the Pi-hole server as the Primary DNS server.
Leave the Secondary DNS blank.
Reference doc is here