Docker Notes
- 1. What is Docker
- 2. Containerization Features
- 3. Docker Image
- 4. Docker Hub
- 5. Docker Engine
- 6. Docker File
- 7. Docker Version Commands
- 8. Docker Image Commands
- 9. Docker Lifecycle Commands
- 10. Docker Status commands
- 11. Docker Cleanup Commands
- 12. Docker Container Examples
- 13. Docker Stack Examples
1. What is Docker
-
Docker is a container platform for developers and sysadmins to build, run, and share applications with containers.
-
It runs in the cloud via a cloud provider or on laptops and data centers VMs.
-
It is used to containerize legacy apps.
-
It is used to build new microservices apps.
2. Containerization Features
- Flexible
-
Even the most complex applications can be containerized.
- Lightweight
-
Containers leverage and share the host kernel, making them much more efficient in terms of system resources than virtual machines. It runs a discrete process, taking no more memory than any other executable, making it lightweight.
- Portable
-
You can build locally, deploy to the cloud, and run anywhere.
- Loosely coupled
-
Containers are highly self-sufficient and encapsulated, allowing you to replace or upgrade one without disrupting others.
- Self Contained
-
Guarantees that applications will always run the same regardless of where they are deployed.
- Scalable
-
You can increase and automatically distribute container replicas across a datacenter.
- Secure
-
Containers apply aggressive constraints and isolations to processes without any configuration required on the part of the user.
- Isolation
-
Each container interacts with its own private filesystem provided by a Docker image. An image includes everything needed to run an application - the code or binary, runtimes, dependencies, and any other filesystem objects required.
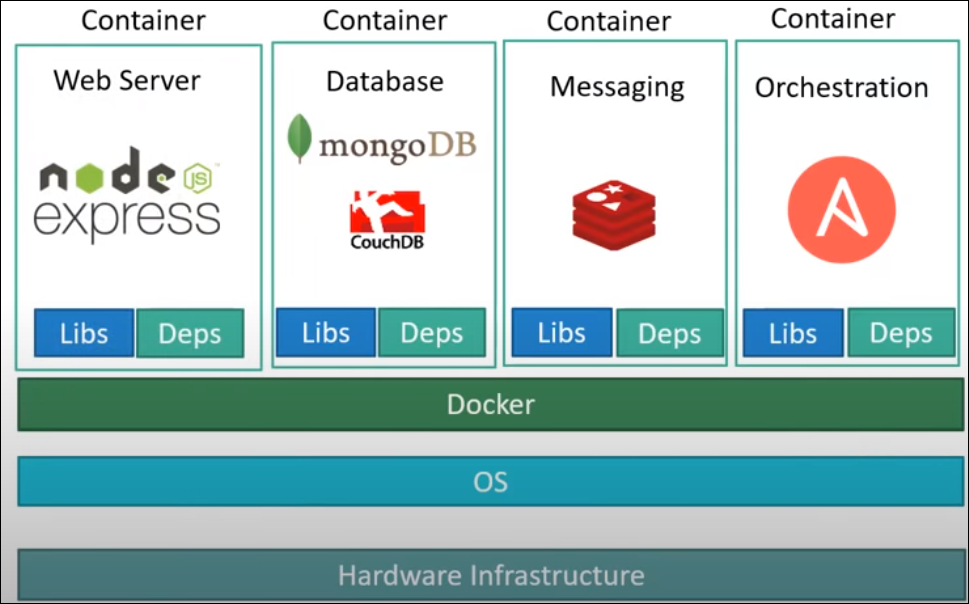
The following is a graphical representation of several containers hosted by Docker and their relationship to the host system:
3. Docker Image
-
An image includes everything needed to run an application in a container - the code or binary runtimes, dependencies, and any other required filesystem objects.
-
It also contains other configuration for the container, such as environment variables, a default command to run, and other metadata.
-
An image can be used to instantiate multiple container instances.
4. Docker Hub
It is the world’s largest repository of container images with an array of content sources including container community developers, open source projects and independent software vendors (ISV) building and distributing their code in containers.
-
Docker Hub is a repository service provided by Docker for finding and sharing container images with your team.
-
You can search the
Docker Hubrepository from here.
5. Docker Engine
-
Allows you to build, run, and share containerized applications on Linux/Windows/Macs.
5.1. Install Docker Engine
5.1.1. Windows Desktop
-
Install Windows Subsytem for
(WSL 2)Linux kernel -
Install Docker Desktop.
6. Docker File
-
This file must be named Dockerfile. It describes the build process for creating an image.
-
It contains necessary commands for building an image and running the application.
6.1. Docker File Commands
| A full reference can be found here |
- ADD
-
TBA
- COPY
-
TBA
- ENV
-
TBA
- EXPOSE
-
TBA
- FROM
-
TBA
- LABEL
-
TBA
- STOPSIGNAL
-
TBA
- USER
-
TBA
- VOLUME
-
TBA
- WORKDIR
-
TBA
8. Docker Image Commands
8.2. image ls
-
List all downloaded images:
docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE wordpress latest c01290f258b3 4 days ago 550MB camunda/camunda-bpm-platform run-latest c1b49a5b4227 11 days ago 243MB stonebranch/universal-agent latest eca81e31c6a3 12 days ago 1.53GB busybox latest 388056c9a683 12 days ago 1.23MB docker/getting-started latest 3ba8f2ff0727 4 weeks ago 27.9MB
8.4. image rm
-
Removes a docker image that is referenced by its Image ID:
sudo docker image rm <image ID>
8.5. image prune
-
Prune will remove all dangling images and any unused images that are not referenced by any running or stopped containers
Commandsudo docker image prune -aExamplesudo docker image prune -a WARNING! This will remove all images without at least one container associated to them. Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y Deleted Images: untagged: docker.repo.xackleystudio.com/com-xs-spa-accounting@sha256:0260a30a67ad213f3fb8e24a11d5fdcc65f5d3ca43fd2221b8a13c6aa31f86b7 deleted: sha256:5b1805a2051a89e5c372e6062f301160e65c085220b2fe56bb6d4fc5733f174b deleted: sha256:d7abd446fefb3853b30657882d81572a4ed157b53a5d6de2288b439cb64098d7 untagged: docker.repo.xackleystudio.com/com-xs-spa-accounting@sha256:353148f8ca972224d21c589dd030f7cc18bd7da941e4b49ef2da62d24732e867 deleted: sha256:fed35a7838e85cf02163b0e70872828e3b279c63b93a0a1e589f10927efb7647 deleted: sha256:07ca8a1e9a6e1bcb9f5afe9b5b191717381121f54fe720f53729d989b57072bf Total reclaimed space: 71.41MB
8.6. system prune
-
Delete all stopped containers and delete all images in the build cache:
docker system prune WARNING! This will remove: - all stopped containers - all networks not used by at least one container - all dangling images - all dangling build cache Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y Deleted Containers: a06c836c2a2eb0c02084bdef480eb936cb396d669d5274dfb3f7af079bf75159 70e0b00f8a13aa75e76b3914c4677fac6d510229d1aeadd7297e97600d340056 Deleted build cache objects: lq8fii44gmb83elngpz08rqyu 43cawslfsqbweb2ls6moacppd 56virr3nlkfplfunck4hbs8pr a3k8smfqg80xk70v768stmogs 5v3cypmqiray0o4ny9wyfx7f3 Total reclaimed space: 400.5MB
9. Docker Lifecycle Commands
9.1. create
-
Instantiate a container from an image:
docker create hello-world 70e0b00f8a13aa75e76b3914c4677fac6d510229d1aeadd7297e97600d340056 docker ps --all CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 70e0b00f8a13 hello-world "/hello" 33 seconds ago Created zen_bartik
9.2. start
-
Starts an already instantiated container by running the container’s
startupcommand.docker start -a 70e0b00f8a13aa75e76b3914c4677fac6d510229d1aeadd7297e97600d340056 Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly. docker ps --all CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 70e0b00f8a13 hello-world "/hello" 2 minutes ago Exited (0) 2 minutes ago zen_bartik
9.3. run
-
This command is a combination of the
createandstartcommands:docker run -t -d hello-world (1) Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally (2) latest: Pulling from library/hello-world (3) 2db29710123e: Pull complete Digest: sha256:507ecde44b8eb741278274653120c2bf793b174c06ff4eaa672b713b3263477b Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest ccd3e66e756adbebed35e0d6c8f821eb784537c55db67c40750092d028c468ac docker ps --all (4) CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES ccd3e66e756a hello-world "/hello" 5 seconds ago Exited (0) 4 seconds ago friendly_yonath (5) docker run -t -d --name MyHelloWorld hello-world (6) d2f9a1302796c264da5d80544e83b5e626aa7a60f93ec5b950408df39d087ae6 docker ps --all (7) CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES d2f9a1302796 hello-world "/hello" 7 seconds ago Exited (0) 5 seconds ago MyHelloWorld (8) ccd3e66e756a hello-world "/hello" 49 seconds ago Exited (0) 48 seconds ago friendly_yonath (9)1 Instantiate a container based on the hello-world docker image. 2 Docker image is not in the local Docker cache. 3 Download the Docker image via the internet. 4 List containers. 5 Here’s the instantiated container with a randomly assigned name. 6 Again, instantiate a container based on the hello-world docker image but name the container MyHelloWorld. 7 List containers. 8 The recently created docker image with the provided name of MyHelloWorld. 9 The initial docker image with a randomly assigned name.
9.4. stop
-
Gracefully shutdown a container by name. The container is allowed a max of 10 seconds for a graceful shutdown. If it needs more than 10 seconds, a kill will be executed:
docker ps (1) CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 2d23f4790668 busybox "ping google.com" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes cranky_elgamal (2) docker stop cranky_elgamal (3) cranky_elgamal docker ps (4) CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES1 Get a listing of running containers. 2 The name of this container is cranky_elgamal.3 Stop the container named cranky_elgamal.4 The container is no longer running.
9.5. kill
-
Immediately shutdown a container via its name:
docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 7d968dee18b5 busybox "ping google.com" 3 seconds ago Up 3 seconds crazy_lehmann (1) docker kill crazy_lehmann crazy_lehmann docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES1 The name of this container is crazy_lehmann
9.6. exec
-
Execute a command inside a container. In this example will interactively run the
bashcommand which will give us shell access within the ubuntu container:docker run -dt ubuntu (1) 541e05be7d9c259ce443f91705c0064daaeb52ebfcfc9ea7826a4bbadbde32e5 docker ps (2) CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 541e05be7d9c ubuntu "/bin/bash" 5 seconds ago Up 4 seconds distracted_hopper (3) docker exec -it 541e05be7d9c bash (4) root@541e05be7d9c:/# whoami (5) root (6) root@541e05be7d9c:/# uname -a (7) Linux 541e05be7d9c 5.4.72-microsoft-standard-WSL2 #1 SMP Wed Oct 28 23:40:43 UTC 2020 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux (8) root@541e05be7d9c:/#1 Start a detached instance of an ubuntu docker image. 2 View running containers. 3 The ubuntu container has an ID of 541e05be7d9c. 4 Start a bashshell in the ubuntu container.5 Run the whomamicommand inside the container.6 The whoamicommand responds with root.7 Now we’ll run the uname -acommand.8 The results of the uname -acommand.
10. Docker Status commands
10.1. ps
List currently running docker images and related containers:
docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f65fb9bcd3ec stonebranch/universal-agent:latest "./ua_entrypoint" About a minute ago Up About a minute 7878/tcp, 7887/tcp My-UAG110.2. ps --all
List all docker images and related containers:
docker ps --all
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f65fb9bcd3ec stonebranch/universal-agent:latest "./ua_entrypoint" 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes 7878/tcp, 7887/tcp My-UAG111. Docker Cleanup Commands
11.1. system prune
This will remove unused images and folder in the /var/lib/docker/overlay2 directory.
sudo docker system prune -a -fmattosd@v-Ubuntu00:~$ sudo docker system prune -a -f
[sudo] password for mattosd:
Deleted Networks:
docker-compose_default
docker-devops-stack_default
Deleted Images:
untagged: ubuntu:latest
untagged: ubuntu@sha256:34fea4f31bf187bc915536831fd0afc9d214755bf700b5cdb1336c82516d154e
deleted: sha256:df5de72bdb3b711aba4eca685b1f42c722cc8a1837ed3fbd548a9282af2d836d
deleted: sha256:629d9dbab5edeac7fa51f205839d7f9bb629a5e83548da3a183fb66c22fe7af7
Total reclaimed space: 77.83MB12. Docker Container Examples
-
This section will guide you through downloading various public Docker images and launching them as containers.
-
An installed and configured Docker Engine / Podman will be required in order to execute the examples.
12.1. Docker - Getting Started
Click here for the Getting Started document.
12.2. Ubuntu
Click here for the Ubuntu document.
12.3. WordPress
Click here for the WordPress document.
12.4. GitLab
Click here for the GitLab document.
12.5. Camunda
Click here for the Camunda document.
12.6. Universal Automation Center Agent (UAC)
Click here for the UAC document.
12.7. Portainer
Click here for the Portainer document.
12.9. Mail Server
-
Maybe Mailu?
-
Maybe docker-mailserver?
13. Docker Stack Examples
These are not really Docker Stacks - it’s Docker Compose at the moment
|
13.1. DevOps
Click here for the DevOps document.